Type of Transport Where a Cell Takes in a Large Particle, Like Food
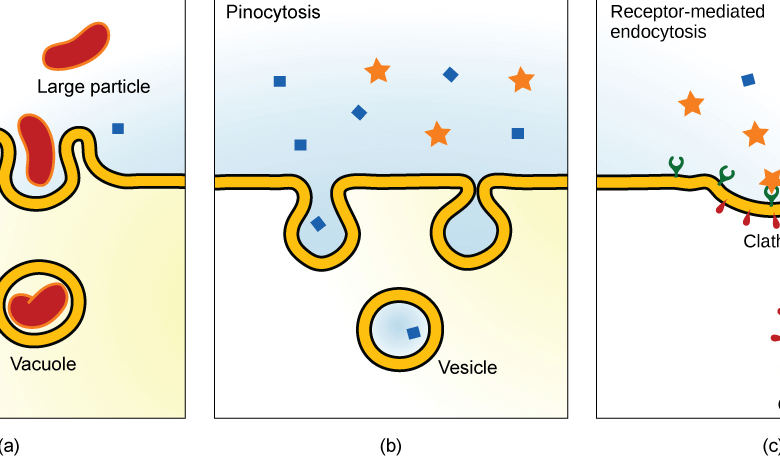
Type of Transport Where a Cell Takes in a Large Particle, Like Food a crucial cellular transport mechanism through which cells internalize large particles, including nutrients and pathogens. This intricate process begins with the recognition of target particles via specific membrane receptors, followed by the formation of pseudopodia that envelop the particle. Once sequestered within a phagosome, the material undergoes processing, underscoring phagocytosis’s significance in cellular nutrition and immune responses. However, the implications of this process extend beyond basic cellular functions, raising intriguing questions about its role in health and disease. What additional layers of complexity does this mechanism reveal?
Overview of Phagocytosis
In the realm of cellular transport mechanisms, phagocytosis represents a critical process through which cells engulf and internalize large particles, such as pathogens or cellular debris.
This mechanism is essential for maintaining cellular nutrition and supporting the immune response.
Mechanism of Particle Engulfment
Particle engulfment, a hallmark of phagocytosis, involves a series of intricate and highly regulated steps that enable the cell to effectively internalize large particles.
Initially, particle recognition occurs via specific receptors on the cell membrane, facilitating binding.
Subsequently, the cell membrane extends around the particle, forming pseudopodia that encase it, ultimately leading to membrane fusion and internalization within a phagosome for processing.
Importance in Cellular Functions
Cell transport mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating essential physiological processes.
They are integral to cellular nutrition, enabling uptake of macromolecules that fuel metabolic activities.
Furthermore, these mechanisms significantly contribute to the immune response by allowing cells to engulf pathogens and debris, thereby ensuring organismal health.
Effective transport systems are vital for optimal cellular function and overall biological integrity.
Read Also Art:Kvgwpzuztw0= Apollo
Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology
The mechanisms of cell transport have significant implications in the fields of medicine and biotechnology, influencing therapeutic strategies and innovative treatments.
Specifically, understanding endocytosis enhances therapeutic applications by facilitating targeted drug delivery.
Moreover, advancements in vaccine development leverage these transport mechanisms to improve antigen uptake and immune response, ultimately leading to more effective immunization strategies.
This synergy underscores the importance of cellular transport in modern healthcare solutions.
Conclusion
Type of Transport Where a Cell Takes in a Large Particle, Like Food, phagocytosis serves as a vigilant sentinel, tirelessly patrolling the boundaries of life. It embodies the artistry of nature, where cells, akin to skilled artisans, craft a harmonious balance between nourishment and defense. This intricate process not only sustains cellular vitality but also fortifies the organism against insidious threats. Thus, phagocytosis emerges as a cornerstone of biological integrity, a testament to the elegant interplay between survival and adaptation in the ever-evolving landscape of life.




